IT security and cybersecurity are concerned with the safety and security of your computer’s data. Thus, both terms are often used interchangeably. However, IT security and cybersecurity are not the same thing.
Cybersecurity mainly deals with protecting data from cyber threats, whereas IT security takes a complete approach to secure the organisation’s digital and physical assets.
In this blog, we’ll briefly discuss the major differences between cybersecurity and information technology (IT) security and how you can ensure your company is effectively secured against cyberattacks.

IT Security vs Cyber Security: Comparison Table
The following table explores the difference between cyber security and IT security:
| IT security | Cyber security | |
| Protection | Focuses on protecting sensitive information from any kind of threat. | Focuses on protecting the software, hardware, or online technology a company uses, from cyberattacks. |
| Format | Use physical formats as well as digital formats. | Use digital formats. |
| Functionality | Protects information from unauthorised access, disclosure use, modification, disruption or destruction. | Protects information from cybercrimes, cyber frauds, cyber threats and law enforcement. |
| Main focus | IT security focuses on information assets such as confidentiality, integrity, and availability. | Cybersecurity focuses on protecting social media accounts and personal details. |
| Task of Professionals | IT security analysts find strategies, policies, and solutions and manage risk. | Cybersecurity professionals perform data recovery, report security metrics and install antimalware software. |
| Approaches and methodologies | Access control, Authentication, Encryption, Firewalls, Antivirus, Backup and Disaster recovery, etc. | Network security, Application security, Cloud security, Incident Response, Threat Intelligence, etc. |
| Compliance requirements | Requires compliance with relevant IT security standards, data privacy laws, and industry-specific regulations. | Requires compliance with data protection laws, industry regulations and cybersecurity frameworks. |
This can be summarized as “All cybersecurity is IT security, but not all IT security is cybersecurity.”
What is IT security?
IT security or information technology security encompasses all physical as well as digital data security methods and applications. Its primary goal is to ensure data integrity and security during storage and transfer.
The important components of IT security are known as the CIA triad, which stands for:
- Confidentiality: Prevents unauthorised parties from accessing confidential and private information.
- Integrity: Ensures that information is only updated in a specific and authorised manner.
- Availability: Ensures that the system responds quickly and authorised users can access services.
IT security also aims to ensure that company data is safe, secure and reliable as well as covers a broad area of cyber security. Due to its wide scope, it is easy to be an IT expert without specialising in cyber security. IT security duties may include:
- Physical security: These controls are intended to prevent unauthorised individuals from getting physical access to sensitive data components.
- Technical security: These controls protect information kept on the network. It also protects information as it transits in or out of the network.
- Administrative security: These controls refer to security rules and practices that control user activity on a network.
What is Cyber security?
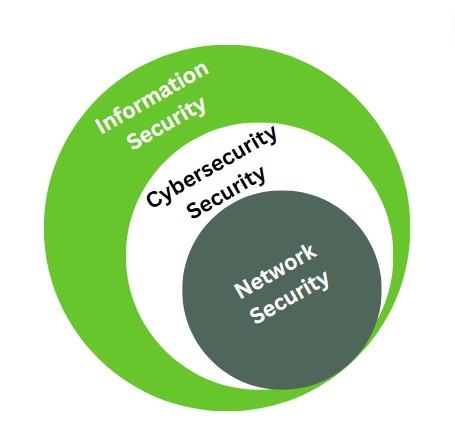
Cyber security is a subset of information security that mainly deals with the information stored in the digital domain. Just like IT security, it aims to keep data secure but focuses more on protecting electronic information. This includes information from networks, servers, computers, tablets, workstations, and mobile devices.
Cyber security does not concern the physical security of devices or locations but rather where data is now, where it is going, where it is coming from, and how safe it is.
All cyber security policies are designed to prevent unauthorised individuals from accessing electronic data and to protect against cyberattacks. To do this, cyber security professionals employ a variety of procedures and standards, including detecting important data and examining weak areas. It assists in assessing data security threats and enhances an organisation’s security.
IT Security vs Cyber Security: Major Differences Explained
Here are the significant differences between IT security and cyber security :
Scope
IT security safeguards an organisation’s information systems, infrastructure, and technology. It includes safe network management, database security, access control, as well as hardware and software component security.
On the other hand, cybersecurity safeguards not only information systems but also data, networks, programs, and devices from cyber threats such as hacking, data breaches, malware, and other forms of cyber attack.
Protection
IT security focuses on protecting confidential information from internal threats while also ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data systems and assets within a business. Additionally, it ensures that unauthorised individuals do not obtain access to critical data or affect the performance of IT systems.
However, cyber security has a broader reach because it includes external threats. It also focuses on safeguarding systems and data against external attackers who exploit flaws and use a variety of attack strategies.
Approaches and methodologies
IT security uses a variety of approaches and best practices to protect IT infrastructure and networks. This includes the implementation of firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption techniques, access controls, and user authentication processes.
Nevertheless, cyber security uses similar principles but focuses on practical measures such as threat intelligence and vulnerability assessments. Includes incident response plans, risk management methods, and personnel training to help mitigate cyber security threats.
Techniques implemented
IT security professionals make data recovery plans that provide guidelines for the organisation to follow in the event of an emergency to maintain business continuity. Recovery plans might involve things like transferring and storing data in the cloud and developing a framework for keeping IT operations running after natural disasters or other disturbances. IT security experts typically test security measures before implementing them.
Cyber security professionals ensure software upgrades, manage passwords and implement antivirus and firewalls. Two-factor authentication is frequently used in cybersecurity policy for getting access to software, devices, or other network-stored data.
Do You Need Both IT Security and Cybersecurity?
You will need to have both cybersecurity and IT security in place, as one cannot exist without the other. If you currently have a cybersecurity team, you are already dealing with some aspects of IT security. However, not all components of IT security are required in today’s cloud-based environment.
Companies no longer need to keep their servers on-site and may instead use cloud servers to manage their networking and data storage requirements. These tasks are transferred to the cloud by establishing cybersecurity systems capable of handling them.
When it comes to the digital space, you must maintain a cybersecurity infrastructure to protect your data. This includes monitoring traffic entering and exiting your environment, establishing and maintaining data protection policies, protecting devices on your network from malware and other forms of attack, installing computer security software, and many other responsibilities.
Conclusion
IT security and cybersecurity are two important and complementary fields. Both are essential for protecting computer systems and data from unauthorised access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. However, there are some key differences between the two. IT security refers to a wide range of methods, policies, and practices that protect digital assets. Ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information and technological resources. On the other hand, cybersecurity is concerned with the protection of systems and digital data against cyberattacks transmitted via networks or the internet. Overall, IT security and cybersecurity are complementary, reinforcing one another to completely protect against security risks. Thus, every organisation needs to implement IT security controls.
NSW IT support offers complete services, including cybersecurity and IT security. Contact us today to learn how we protect your business and provide exceptional IT Support at every step.