The integration of IoT is not just a convenience but a game-changer. From optimising network performance to enhancing user experiences, the benefits are vast, but challenges are present. Virtual meetings become immersive as IoT enhances audio-visual quality and ensures a lag-free experience. Enhanced telecommunication networks prioritise data traffic, guaranteeing smooth and uninterrupted connectivity for critical tasks.
In simple terms, the Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices, objects, or “things” that communicate and exchange data with each other through the Internet. These devices are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies, allowing them to collect and transmit data.
IoT in the Telecommunication Industry
In the telecommunications industry, IoT plays a transformative role by integrating smart devices and communication technologies. This convergence enhances connectivity, efficiency, and the overall capabilities of telecommunications networks. IoT in telecommunications involves the deployment of connected devices, sensors, and systems that gather and share data, enabling diverse applications.
In the telecom sector, IoT applications include smart homes, smart cities, industrial automation, healthcare monitoring, and more. These applications leverage the capabilities of IoT to improve communication, automate processes, and enhance the overall user experience.
Imagine being stuck in rush hour, juggling calls and emails. Suddenly, your AI assistant seamlessly routes urgent calls to your smartwatch, schedules follow-up emails, and highlights relevant data on a personalised dashboard. This is the magic of smart technology in telecom, making every click and every connection work smarter, not harder.
Doesn’t this sound like something you’d want in your life? Ready to embrace the enchantment of smart technology every day? Reach out to NSWITs today and take your connectivity to new heights with VoIP technology. Your connected future is just a step away!
But wait, there’s more to discover! Dive more into this blog, and let it be your gateway to a profound understanding of how IoT is reshaping the landscape of the telecommunications industry.
What are the 4 types of IoT?
The term IoT encompasses a wide range of applications and use cases. While it’s challenging to categorise IoT into rigid types, there are four commonly recognised categories that represent different aspects of IoT for telecom:
1. Consumer IoT (CIoT): CIoT focuses on consumer-oriented applications, enhancing the functionality and connectivity of everyday devices.
- Examples: Smart homes, wearable devices, connected appliances, and personal gadgets.
2. Commercial IoT (CIoT): CIoT is centred around applications within business and industrial settings, aiming to improve operational efficiency and decision-making.
- Examples: Industrial automation, smart agriculture, logistics, and supply chain management.
3. Enterprise IoT (EIoT): EIoT involves the deployment of IoT solutions within large organisations, impacting various aspects of their operations.
- Examples: Asset tracking, energy management, and facility monitoring in large enterprises.
4. Industrial IoT (IIoT): IIoT focuses specifically on applications within industrial sectors, integrating sensors and connectivity to enhance industrial processes.
- Examples: Predictive maintenance in manufacturing, smart grids in energy, and remote monitoring of machinery.
Benefits of IoT in Telecom Industry
A. Improved connectivity and communication
- The integration of IoT in the telecom sector significantly enhances connectivity by optimising network performance. This ensures that data transmission is reliable and seamless.
- IoT-driven improvements in communication enable faster and more efficient data exchange, benefiting both end-users and businesses.
- With increased connectivity, telecommunication operators can meet the growing demand for real-time communication, supporting applications ranging from video conferencing to smart devices.
B. Enhanced customer experience
- IoT contributes to an elevated customer experience by facilitating personalised and smarter services. Connected devices, such as smart homes and wearables, create a more tailored and responsive environment for users.
- The data insights provided by IoT enable telecommunication operators to understand user preferences, delivering more relevant and customised services.
- Improved customer experiences lead to increased satisfaction, loyalty, and a positive brand image for telecom companies.
C. Operational efficiency and cost savings
- The implementation of IoT allows for efficient resource management within the telecom infrastructure. This optimisation leads to cost savings by reducing unnecessary expenses and improving overall operational productivity.
- Real-time data insights provided by IoT sensors enable telecommunication operators to identify areas for improvement, streamline processes, and allocate resources more effectively.
- Predictive maintenance, made possible by IoT, minimises downtime and lowers maintenance costs, contributing to significant operational efficiency gains.
D. New revenue streams and business opportunities
- IoT implementation opens up new revenue streams for telecommunication operators by diversifying their service offerings. This could include IoT-based solutions for businesses, smart city initiatives, and other innovative services.
- Telecom companies can tap into emerging market opportunities for IoT and capitalise on the demand for cutting-edge technologies, creating business opportunities that go beyond traditional connectivity services.
- The ability to offer unique and value-added services positions telecom operators to explore and leverage evolving market trends and consumer demands.
Schedule a free consultation with NSWITs to discuss your specific IoT needs and discover how we can help you achieve your goals. We will show you how to unlock the power of IoT architecture for your business or home.
E. Innovative service offerings
- The integration of IoT in the telecom organisation allows for the introduction of innovative services that extend beyond conventional voice and data offerings.
- IoT-driven solutions, such as smart home automation, connected vehicles, and industrial IoT platform, create new and diverse service offerings.
- These innovations not only cater to consumer needs but also provide opportunities for telecommunication companies to enter niche markets and differentiate themselves in a competitive landscape.
- By embracing innovative service offerings, telecom operators can benefit from IoT, stay at the forefront of technological advancements, and meet the evolving demands of their customer base.
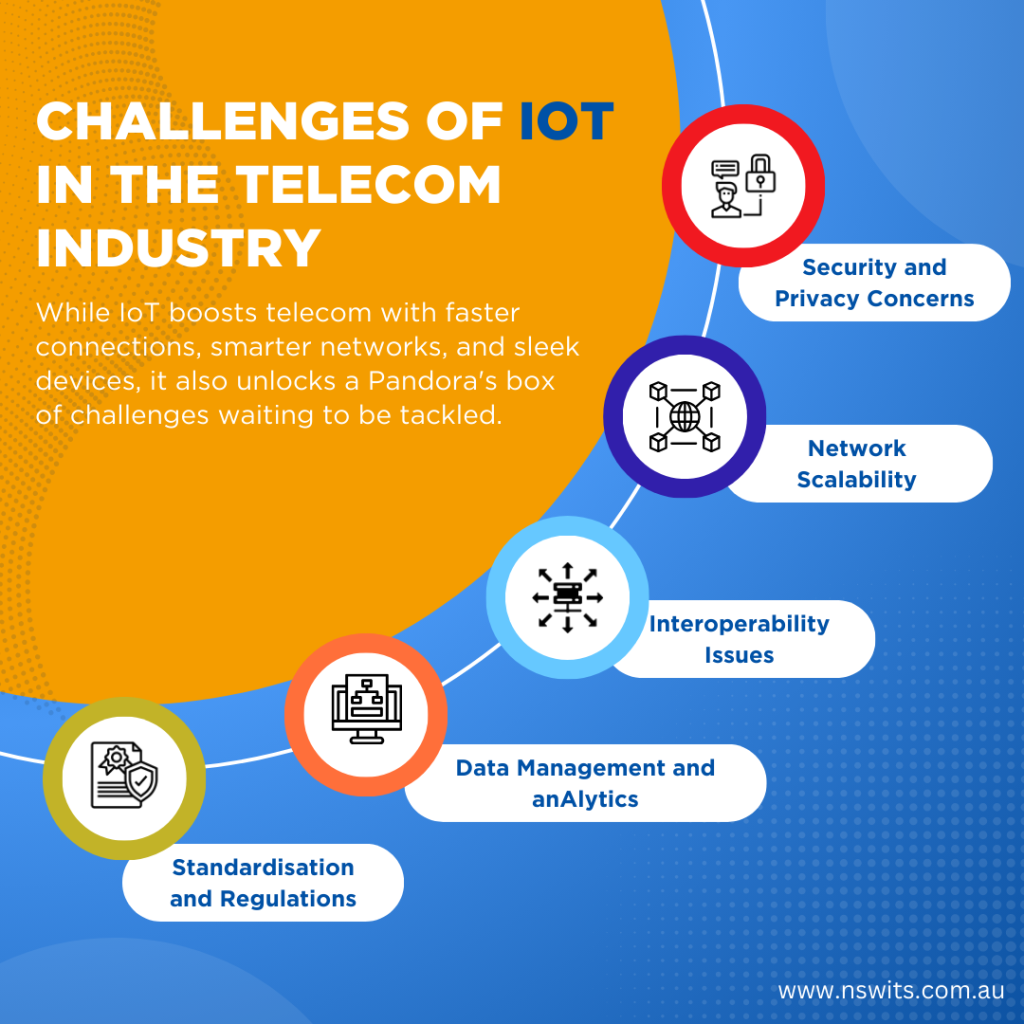
Challenges of Implementing IoT in the Telecom Industry
Security and Privacy Concerns
The telecom business is facing complex security challenges due to the integration of the Internet of Things. As IoT devices are interconnected, they become vulnerable to cyber threats which can compromise their security. Privacy concerns also arise since these devices collect extensive data. This raises questions about how this data is processed, handled, and shared. To ensure that sensitive information is protected and the trust of users is maintained, it is crucial to establish robust security measures and encryption protocols and to adhere to privacy regulations.
Network Scalability
The growing number of connected devices poses scalability challenges for telecom networks. It is essential to guarantee that the infrastructure can effectively handle the increasing data traffic and seamlessly integrate new devices without compromising performance. IDEMIA projects that by 2025, the IoT platform will produce over 2 zettabytes of data, primarily from consumer electronic devices. Maintaining a high level of service quality depends heavily on the critical factor of network scalability, which is crucial for supporting the continuous growth of the expanding IoT ecosystem.
Interoperability Issues
The market is filled with various types of IoT technologies and devices, which poses challenges in terms of interoperability. For telecom service providers, ensuring seamless communication and compatibility across multiple devices and platforms is a significant challenge. The absence of standardised protocols can lead to integration issues, which can impede the development of a unified and effective IoT ecosystem.
Data Management and Analytics
The effective management and analysis of the massive amount of data generated by IoT devices is essential. Forbes reports that a substantial 73% of the data collected by enterprises goes unused, revealing a significant challenge associated with IoT. Telecommunication companies must invest in advanced analytics tools to extract valuable insights from the vast datasets produced by these devices. The challenge is to process, analyse, and translate actionable insights from the diverse and often real-time streams of data.
Standardisation and Regulations
The implementation of IoT in the telecom sector is complicated due to the lack of standardised protocols and regulations. The use of different standards among devices and technologies can lead to challenges in interoperability, resulting in a fragmented IoT landscape. It is also difficult for telecom operators to navigate a constantly changing regulatory environment, particularly with respect to data privacy and security. They must stay compliant with the evolving regulations to ensure consistency and avoid complications.
Can IoT work without the internet?
I bet this question must have been on your mind with all these challenges of IoT around. Am I right?
IoT devices can operate without a direct internet connection. However, the dependency on internet connectivity can be considered a limitation for IoT software.
Working Without Internet:
- Local Networks: IoT devices can communicate with each other within a local network, enabling them to function without connecting to the broader internet.
- Mesh Networks: Certain IoT devices create mesh networks, enabling them to share data among themselves, even when internet connectivity is unavailable.
- Edge Computing: IoT devices have the capability to process data locally or within a local gateway, minimising the dependence on constant internet access.
Limitations:
- Limited Functionality: Many IoT applications benefit from internet connectivity, offering features like remote monitoring, data analytics, and cloud-based services. Without internet access, these functionalities may be restricted.
- Dependency on Cloud Services: Some devices heavily rely on cloud-based services for data storage, updates, and remote management. Lack of internet connectivity can hinder these aspects.
- Reduced capabilities: Features like remote control, software updates, and access to broader information or cloud services might be unavailable.
Ready to launch an application of IoT for telcos? Embrace the transformative power of IoT with NSWITs by your side. Let’s shape a smarter, more connected world together! Contact Us!
Future Opportunities for IoT in for Telecom Industry
The Internet of Things (IoT) presents significant future opportunities for the telecom industry. As per the markets and markets, the IoT market size is projected to reach USD 650.5 billion by 2026, at a CAGR of 16.7% during the forecast period, 2021-2026.
As more devices become connected, there will be a growing demand for reliable and high-speed networks to support the massive influx of data. Here are some key opportunities that using the Internet of Things brings to telecommunication companies.
- 5G and Edge Computing: The deployment of 5G networks and edge computing technologies will significantly enhance the capabilities of IoT. Telecom organisations can leverage these technologies to deliver ultra-low latency, high bandwidth, and edge processing capabilities, enabling real-time data processing and time-sensitive applications like autonomous vehicles and smart city infrastructure.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): The application of AI and ML allows for the analysis of IoT data, recognising patterns and making predictions. This facilitates proactive maintenance, personalised services, and enhanced decision-making capabilities. Deloitte estimates indicate that 38% of Australian organisations are making substantial investments in AI. The widespread adoption of cloud technology in 2020 has granted telecommunications companies in the country greater control over their data, resulting in increased profit.
- Data Analytics and Insights: With the increasing volume of data generated by IoT devices, telecom companies have the opportunity to extract valuable insights through advanced analytics. These insights can help businesses make informed decisions, improve operational efficiency, and provide personalised services to their customers.
- Enhanced Connectivity: According to Statista, the number of IoT devices globally is expected to skyrocket to 29 billion by 2030, almost three times the 2020 count of around 9.7 billion. The proliferation of IoT devices, such as smart homes, wearables, and industrial sensors, requires robust and seamless connectivity. Telecom organisations can capitalise on this demand by providing reliable network infrastructure and telecom services that ensure uninterrupted connectivity for IoT products or devices.
- Vertical-Specific Solutions: IoT enables telecom organisations to develop industry-specific solutions tailored to different sectors such as healthcare, transportation, agriculture, and manufacturing. By offering specialised IoT services and platforms, telecom providers can cater to the unique needs of these industries, driving innovation and creating new revenue streams.
-
Don’t miss out on the revolution of IoT! NSWITs has a team of experienced professionals who can help you implement IoT solutions in your VoIP system. With a spectrum of connectivity solutions crafted specifically for IoT—ranging from cellular connectivity to device management and cloud computing, we, as a telecom service provider, can help you make it happen. Contact Us Today!










