When your computer’s fans are constantly spinning at maximum speed, your CPU is being overused. Simultaneously, your computer may hamper. That isn’t very pleasant, especially if you are not doing anything.
Computers are controlled by their CPUs (central processing units), also called processors. A hectic workday can overwhelm a brain, especially if it is swamped by applications too many or demands too much attention from one task. When you’re overworked, you’ll find work difficult. But if you ask too much of your processor directly, your work will slow.
By staying clear of demanding programs, you can avoid the situation. A bug can, however, sometimes occur during a process that causes CPU usage to be stray. Unfortunately, you’ll usually find the cause of the high CPU usage and resolve it quickly.
The following are some bugs and problems that can appear due to high CPU usage, so we are getting to mention the causes and how you can repair it so that it operates appropriately again. Nevertheless, we must first understand.
How can high CPU usage be explained?
CPUs (Central Processing Units) perform most of the work done by computers. Data is processed, and commands are delegated. A CPU-based program or process does not experience any interruption. A faster PC will generally run with a faster processor. You may experience an increase in CPU usage based on what you open. As a result, CPU performance is noticeable within the startup processor in the response time of applications. You may notice that specific orders and actions may take longer to execute when working with CPU-intensive software (e.g. graphics and video editing software).
In other words, poor performance is not always a sign that the CPU has a problem. Alternatively, many CPU-intensive programs could be running concurrently, and the CPU could have reached maximum capacity. For PCs to avoid prematurely being replaced with high-performance models, it is vital to understand CPU usage and its causes.
In what sense is CPU usage measured?
Observing the CPU usage of your running programs will tell you how intensively they are being processed. In terms of percentage, this represents the amount of time a processor core is used to process data. The utilisation of a processor is commonly used to determine how much strain it is currently experiencing and, if necessary, how much capacity it has left.
A comparison is made between the overall operating time and the duration of the performance. Users will experience long loading times if CPU usage is too high. There is a risk of freezing programs if the processor becomes overloaded with too many requests.
Analysing the CPU temperature can provide you with an equivalent picture of processing speed. If the processor is frequently used for background processing or frontend processing, this causes more heat to be generated. Consequently, the computing performance is automatically curtailed, which leads to a gradual decrease in processing power.
What is the best way to display CPU usage?
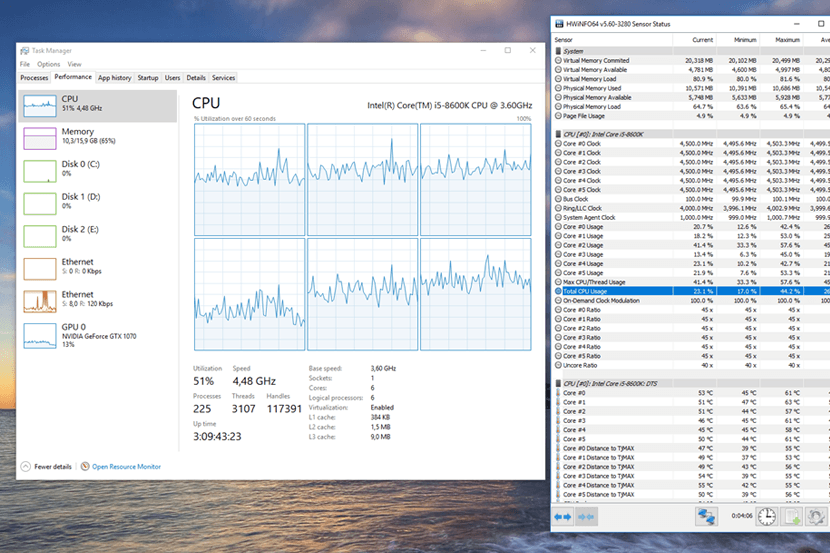
Every operating system provides CPU usage information. You can access Microsoft Windows’ Task Manager by clicking on the Start button. A detailed breakdown of the CPU is currently in use under the “Performance” tab.
Factors contributing to high CPU utilisation
Providing numeric values and data curves can identify if the CPU usage is too high. Often, it is possible to isolate the problem’s source within a brief period.
If you use Task Manager’s “Processes” tab, you can find out how much CPU is being used by looking at the first column of the table. On your computer, you can also view a listing of all the programs and background processes. You can sort the CPU according to intensity by clicking the “CPU” column header. Right-click the program that takes up more CPU than average if you notice it rarely gets used. The CPU might be reduced as a result. These are often immediately removed using the “kill” command.
There are at least some of these reasons to account for higher processor usage than average:
1. CPU-intensive programs and processes:
High-resolution graphics editing programs, DVD burning programs, and applications that convert film and photo formats should all have the high processing power. CPU usage is known to be increased when they are present. If the computer can almost run all those programs, you should run them one at a time and shut down all other apps.
2. Auto-start programs:
When the OS is booted, applications that are launched can have their CPU usage affected. Licenses are often required to run the software necessary to connect hardware components like cameras, MP3 players, and printers. Upon installation, these types of programs will start automatically once they are booted up. You can prevent this from happening by deactivating them via the “Autostart” tab in Task Manager.
3. Viruses:
If you notice extremely high CPU usage of nearly 100 percent but cannot find a cause, an epidemic or other kind of malware might also be to blame. Popular monitoring tools often fail to detect viruses. It is advisable to install a malware scanner immediately if you suspect an epidemic is happening.
4. Browser:
The browser uses considerable CPU power when it opens countless tabs (e.g., each open account). CPU utilisation can also increase if undetected extensions and plug-ins are running in the background. You can regularly check your browser settings to see which attachments and plug-ins you need and deactivate any you aren’t using or rarely using.
What can be done to resolve high CPU usage?
To reduce your CPU usage, follow these methods:
1. Reboot:
Make sure you save any work you are doing on your computer before rebooting. It’s classic troubleshooting advice to turn the computer off and back on again. If this is your first restart for a long time, it may resolve the issue. It could also solve slowdowns in long-running processes by filtering out temporary files.
2. Insufficient background processes:
Background processes always run in the background of a computer without being opened by the user, consuming a significant percentage of processor time. Over time, however, those background processes can pile up and start to require a substantial amount of resources as more applications are downloaded. In addition to stopping these processes, you can also restart your computer to prevent them from being started again automatically once you activate your device.
3. Install An Antivirus:
Many problems can be triggered by high CPU usage, and sometimes they are surprising. An antivirus program could result in slower processing speeds or an outbreak that the software could not prevent.
It’s easy to underestimate how much power your computer uses when you’re constantly scanning your disk drive for potential threats, especially if your device or OS is old. If you experience random lag times, it’s probably due to an antivirus that’s eating up your processor power. Make sure your antivirus works only during times when you are unlikely to use it. You can prevent it by scheduling when it scans your device.
4. Get a RAM upgrade:
A high CPU usage gets defeated through this choice. RAM ports on every system have a maximum capacity. There is an additional port for a 2GB RAM user to put in the RAM manually, and so forth, to solve high CPU usage. Immediately upon installing the RAM. Get started by installing, rebooting, and obtaining going. These steps will help you avoid experiencing the problem of slow computing as you will have more space for your applications to be processed and at a more convenient location.
5. Reduce the Animations running:
It would be best if you disabled Windows’ animations as they can cause your PC to malfunction. Many spirits are run at once by Windows, and each of them can cause harm. You can either click right-click at the beginning button and choose “System” or press the Windows key + X. Next, select the Performance tab under ” Advanced System Settings.” Under the Visual Effects menu, select “Adjust for best performance” to disable all animations. Alternatively, select “Custom” and remove the individual energies you aren’t interested in.
6. Update Drivers:
You can update your drivers if you notice that a process is using too much CPU. A driver is a program that regulates a particular device (such as headphones, a mouse, etc.) attached to your motherboard. Driver updates can go beyond any compatibility or bug issues that are causing high CPU usage.
7. Drivers for security reasons:
You can find the “Check for Updates” button after opening the beginning menu, Settings, then clicking on Updates & Security. There is a possibility that essential drivers will get updated. Manufacturers of graphics cards create utilities (such as NVIDIA GeForce Experience for GPUs) as part of their support for gamers.
Updates to your BIOS version may fix some rare bugs as well. The BIOS is generally not the answer to performance issues (and can even introduce new ones); only update your BIOS if you find a specific BIOS fix to the problem.
8. Reinstalling Windows:
It might be helpful to consider restoring from a point before you noticed the CPU issues. Unfortunately, most people don’t use System Protection since Windows turns it off by default.
In that case, your last resource could also be to reinstall Windows. It will be an extended process but also can potentially resolve CPU usage issues caused by software.
Reinstalling the PC or laptop will uninstall all of your programs, but leave your files alone. Afterwards, you’ll need to reinstall all of the non-Windows programs you work on, and your settings in these are going to be lost unless you save and back them up. In case, copy all of your files either on a drive or through cloud storage services.
As soon as you can start, click the beginning button and select the option “Reset this PC”. The application process can take up to an hour. Click “Get Started”. Your programs will get reinstalled after it is finished.
9. An issue that has a surprising complexity:
If you do not know where to look for it, determining the underlying cause of high CPU usage is often challenging. It may be necessary to upgrade your computer if prime CPU usage persists even when using standard processes. Adding more RAM also reduces your computer’s CPU load, allowing it to store more program data. It may give your CPU a much-needed break by reducing the frequency of internal data transfers and new memory allocations.
The good news is, every user is often made aware of common CPU issues and taught to troubleshoot them, saving IT staff time and allowing production to resume as soon as possible.
If you are still struggling to sort your issue, connect with the professionals of NSW IT service. We are there to support you with the managed IT services. So why take trouble when you are getting professional assistance! Contact Us.